How to Switch to an Electric Vehicle: Everything You Need to Know
Switching to an electric vehicle (EV) is a smart move for the environment and your wallet. With advances in technology, a growing network of charging stations, and enticing federal and state incentives, there’s never been a better time to make the transition. If you’re considering making the switch, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know about electric vehicle ownership.
If you’re in Nevada and looking to finance your switch to an electric vehicle, consider turning to the Nevada Clean Energy Fund (NCEF). We are dedicated to providing affordable financing solutions for clean energy projects, such as installing EV chargers in your home. Explore our resources for homeowners today! Remember, you’re not just making a smart choice for yourself — you’re helping to drive the state toward a greener future.
Common Questions About Electric Vehicle Ownership
What is the range of an EV?
One of the most common concerns about electric vehicles is their range, or how far you can drive on a single charge. Modern EVs have come a long way, with many models offering ranges between 200 and 400 miles. Some high-end models, such as the Tesla Model S, even exceed 400 miles on a full charge.
However, the range can vary based on factors such as driving habits, weather conditions, and the use of features like air conditioning or heating. Fortunately, most EVs provide real-time range estimates, so you’ll always know how much farther you can go before needing to recharge.
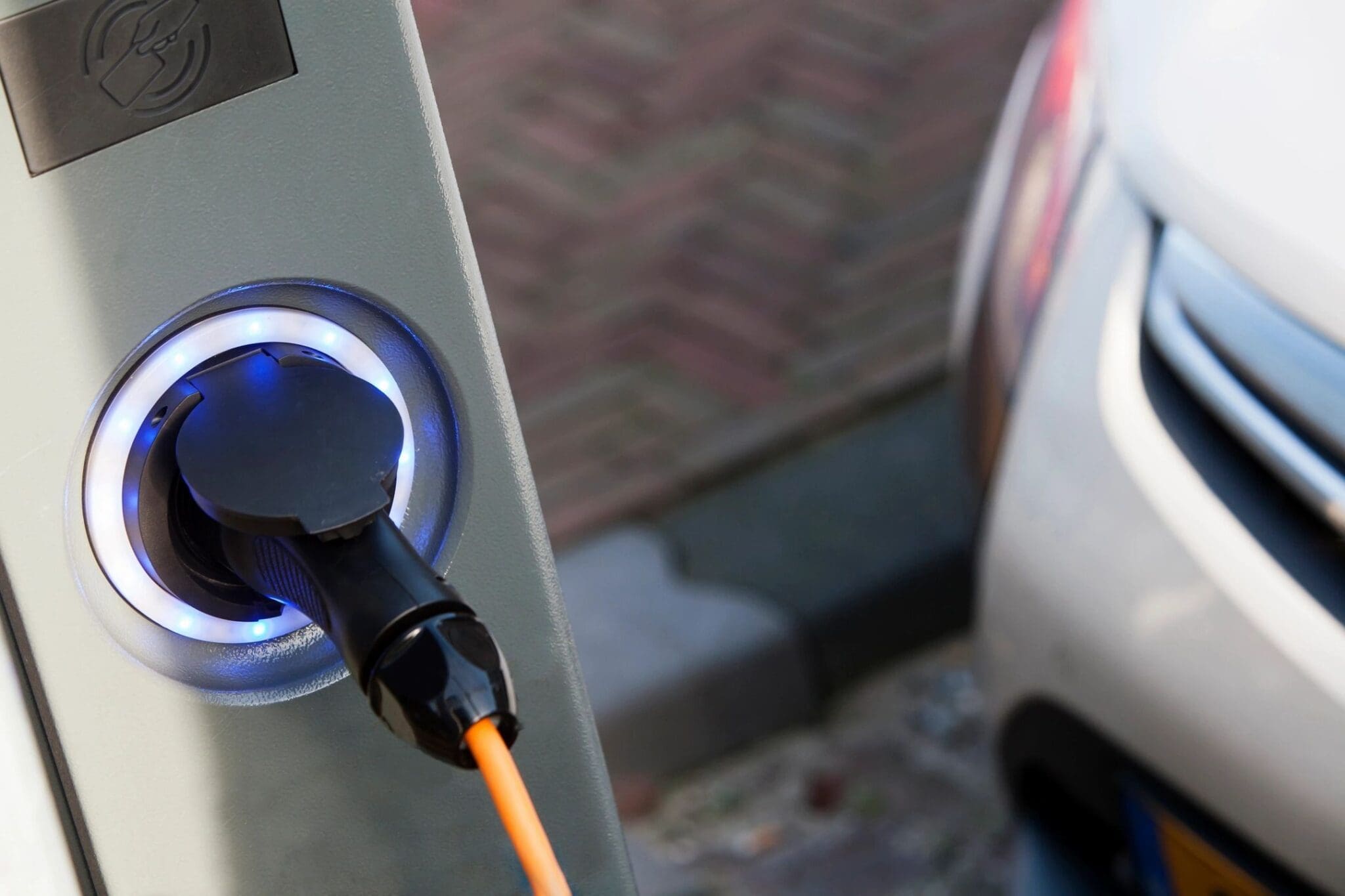
What types of EV chargers are available?
When it comes to charging your EV, there are three main types of chargers:
- Level 1 Charger: This is the standard charging cord that comes with your EV and plugs into a regular 120-volt outlet. It’s the slowest option, adding about 3-5 miles of range per hour, and is best suited for overnight charging at home.
- Level 2 Charger: This charger requires a 240-volt outlet, similar to what your dryer uses. Level 2 chargers can add about 20-60 miles of range per hour, making them a popular choice for home installations and public charging stations.
- DC Fast Charger: This is the fastest charger available, capable of adding 60-100 miles of range in just 20 minutes. Fast chargers are commonly found at public charging stations along highways and in urban areas, making them ideal for quick top-ups on long trips.
Where can I find EV chargers in public?
The network of public charging stations is growing rapidly, making it easier than ever to find a place to recharge. There are several ways to locate public chargers:
- EV Charging Apps: Apps like PlugShare, ChargePoint, and Tesla’s Supercharger map provide real-time information on the location, availability, and pricing of public chargers.
- In-Vehicle Navigation: Many EVs come with built-in navigation systems that include the locations of nearby charging stations.
- Online Maps: Google Maps and Apple Maps now feature EV charging station locations, allowing you to plan your route accordingly.
When searching for public chargers, it’s essential to know that not all chargers are created equal. Some stations offer only Level 2 charging, while others provide fast charging options. Before you arrive, be sure to check the type of charger available to ensure it meets your needs.
What are the costs associated with EV charging?
Charging your EV at home is generally the most cost-effective option, with prices varying based on your local electricity rates. On average in the US, the cost to charge an average-sized battery is $12.29.
Public charging stations may have different pricing structures, including pay per use, subscription models, or even free charging in some locations. DC fast charger stations are typically more expensive than Level 2 chargers, but they offer the convenience of quicker charging times.
Tax Credits and Incentives for EV Ownership
One of the most significant advantages of switching to an electric vehicle is the availability of tax credits and incentives that can significantly reduce your upfront costs.
- Federal Tax Credit: The federal government offers a tax credit of up to $7,500 for new EV purchases. However, this credit begins to phase out once a manufacturer sells a certain number of vehicles, so it’s essential to check your eligibility before buying.
- State Incentives: Many states offer additional incentives, such as rebates, tax credits, and reduced registration fees. In Nevada, federally-funded rebates that we expect to launch in mid-to-late 2025 can help defray the costs of any electrical panel or wiring upgrades that may be necessary to properly install an EV charger in your home.
- Utility Company Incentives: Some utility companies offer rebates for installing home chargers or provide special EV electricity rates. NV Energy, for example, offers a rebate for installing an EV charger in your home.
To take full advantage of these incentives, research the options available in your area and consult with a tax professional to understand how they apply to your situation.
Start Your Clean Energy Journey Today
Switching to an electric vehicle is more accessible and beneficial than ever. With a wide range of options, a growing infrastructure, and substantial financial incentives, the time to make the switch is now. Not only will you enjoy the environmental and financial benefits, but you’ll also be contributing to a cleaner, more sustainable future.
NCEF is a nonprofit organization and green bank that provides financial and technical resources to accelerate clean energy growth in the state, reduce energy costs, create jobs, and meaningfully address climate change. NCEF works with communities, local businesses, schools, governments, tribes, utilities, contractors, lenders, and others to increase access to clean energy opportunities, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, electric vehicles, and energy storage. Learn more about our funding solutions for residents to see how we can help you save on energy efficiency today!